Vinet equation of state
The flow to obtain Vinet equation of state is as follows:
- Assume the Helmholtz free energy (F) as a function of volume (V).
- Obtain the pressure (P) as a function of V with KT0 and KT0' by differentiating F by V.
- Obtain the isothermal bulk modulus at P (KT) by multiplying the V derivative of P by V.
- Obtain the isothermal bulk modulus at zero pressure (KT0) by substituting V = V0 into the formula in Step 3.
- Obtain the P derivative of KT (KT') by differentiating KT by P.
- Obtain KT' at zero P (KT0') by substituting V = V0 into the formula in Step 5.
- Replace unknown parameters in the formula of P in Step 2 by KT0 and KT0' using the formulas obtained in Steps 4 and 6.
Rose et al. [1983] proposed that the binding energy of metals can be well approximated by the following function:
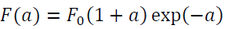
(1)
where a is reduction of the atomic spacing:
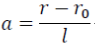
(2)
where r0 and r are the interatomic distances at zero and high pressures, and l is the scaling length. Based on this relation, F of a matter of interest can be expressed as:
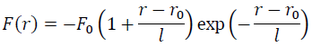
(3)
where F0 is a constant.
By expressing Eq. (3) by the volumes at zero and high pressures, V0 and V as:
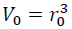
(4)
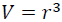
(5)
By substituting Eqs. (4) and (5) into Eq. (3), we have:
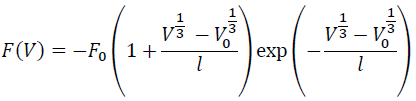
(6)
Therefore, P is:
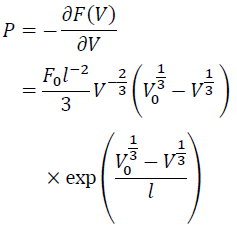
(7)
By differentiating Eq. (7) by V at constant T, we have:
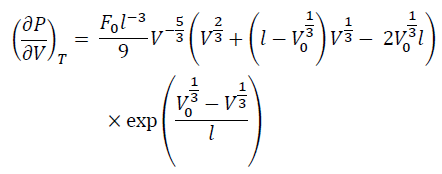
(8)
From Eq. (8), KT is:
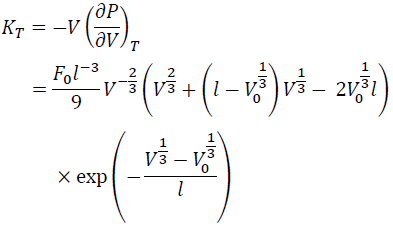
(9)
The KT0 is obtained by substituting V = V0 to Eq. (9):
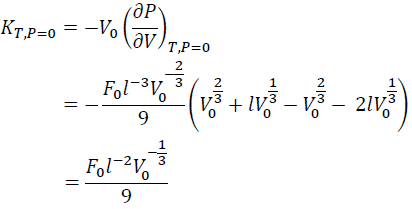
(10)
KT' is obtained by dividing the V derivative of KT by the V derivative of P.
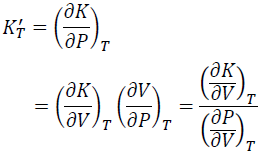
(11)
The V derivative of KT is:
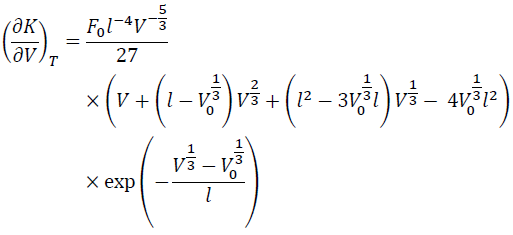
(12)
By substituting Eqs. (12) and (8) into Eq. (11), we have:
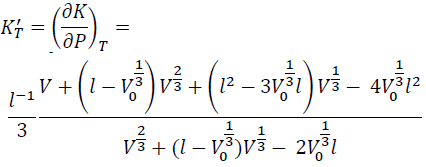
(13)
KT' at zero P (KT0') is obtained by substituting V = V0 into Eq. (13).
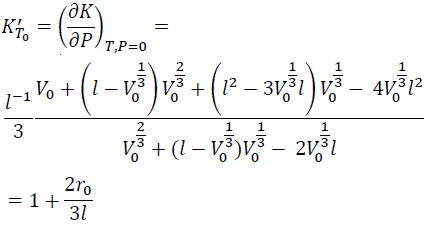
(14)
From Eq. (7) with Eqs. (10) and (14), we have:
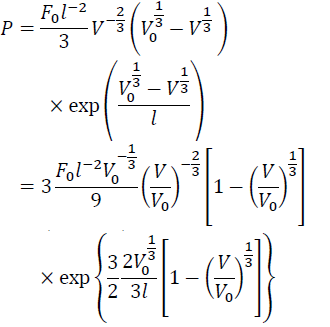
(15)
Finally, we have the Vinet equation of state:
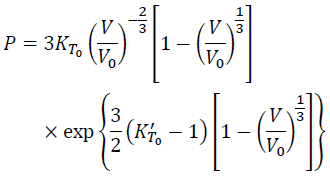
(16)
Thus, the mathematical derivation of the Vinet equation of state is clear from the assumption of the formula of F. Although Rose et al. [1983] proposed the potential (Eq. 1) based on metal data, Vinet et al. [1987] confirmed validity of the equation of state (Eq. 16) by various material such as H2, D2, Xe, Rb, Mo, NaCl, MgO, magnetite and so on.
